Treatment Options
For Japanese beetle certification of plant material according to the Japanese Beetle Harmonization Plan. All treated product must be safeguarded from re-infestation during the flight season. Chemical options are summarized below.
Pesticide Options
In general, pesticides that are labeled in Oregon for treatment of Japanese beetles will be acceptable if they are used according to their labeling. There are some summaries below to assist you. Please contact your nursery inspector if you have specific questions.
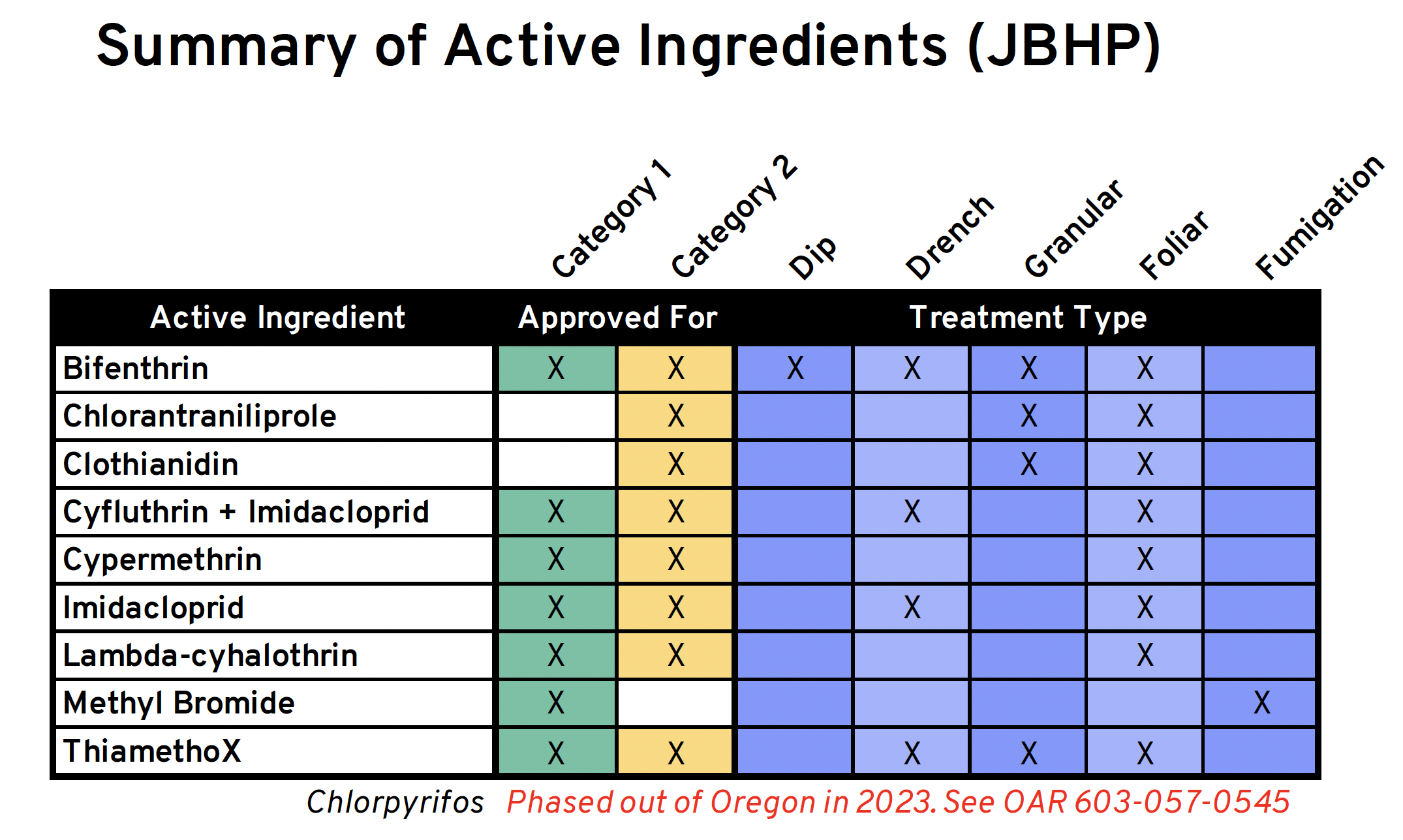
Detailed list of Active Ingredients for Oregon and the JBHP
Please download this file to view all of the pesticide lists.
 JB Treatment table.xlsx
JB Treatment table.xlsx
There are four tabs in this Excel file:- Summary of active ingredients for JB registered in Oregon
- All active ingredients and combinations for JB registered in Oregon
- JBHP Pesticides for Category 1 States
- JBHP Pesticides for Category 2 States
To identify if a product is registered for use in Oregon, please use this search engine:
Pesticide Information Center OnLine (PICOL):
Chemical Treatments table for JBHP:
Treatment options for Category 1 States
1. Dip treatment intended to kill larvae (grubs) in containers or B&B
Only acceptable for material in containers that are 12" in diameter or smaller. B&B material of the same size limit can also be dip-treated, but only if the soil is non-clay. It is presumed that most soils in Oregon will not be suitable for this treatment due to clay content.
- The rooted portion of the container or ball must be completely submerged in pesticide solution for a minimum of 2 minutes or until complete saturation occurs, as indicated by the cessation of bubbling.
- The ambient temperature must be at least 50F at time of dip.
- Upon removal from solution, the plants must be allowed to drain according to label directions.
- During JB flight season (June through Sept.) dip treatments are only good for 2 weeks of certification. If more time passes, an additional treatment would be required.
- Treatments performed outside of the flight season are suitable for certification until the time of the next flight season.
2. Drench treatments for containers to target eggs and first instars of JBThis is considered a preventative treatment. It is only acceptable for material in containers that are 12” in diameter or smaller. Potting media must have started clean (never previously used in agricultural production) and contain no mineral soil or sand.
- Plants grown in field soil then potted into soilless container substrates are not eligible.Plants must be treated prior to JB flight season and certification expires after 16 weeks.
- Plants must be treated prior to JB flight season and certification expires after 16 weeks.
- The goal is to completely drench the surface of the potting media while at the same time limiting run-off through leaching from the bottom of containers. It is recommended to use 1/5 of the container volume as an application rate per container.
- Treated material must be maintained on an impervious barrier.
3. Media (granule) incorporation for containers to target eggs and first instars of JB.This is a preventative treatment prior to potting up. It is only acceptable for plants being potted up into containers 12” in diameter or smaller. Potting media must start clean (never previously used in agricultural production) and contain no mineral soil or sand.
- Plants grown in field soil then potted into soilless container substrates are not eligible.
- Plants being stepped up into treated media must first be treated by drench or dip to clean up any remaining untreated potting media attached to their roots
- Granular insecticide must be thoroughly mixed into batches of potting media prior to potting up.
- Finished plants should be watered at least 2 times prior to shipment.
4. Methyl Bromide FumigationThis option would provide certification for nursery stock of all sizes and media including soil. However, pesticide label limits and plant susceptibility to harm make it an unlikely option.
5. Adult Beetle MitigationDuring flight season between June 1 and September 30th, nurseries are responsible for ensuring that clean stock does not become infected by adults. The JBHP outlines critical control points to monitor. Insecticides that target adults are provided in the JB-labeled product list, to be used for certification if adults are present. There are different insecticides for use on plant material and container (truck/trailer) spaces.
Treatment options for Category 2 States
**Note: New Mexico is not included in this, they have unique requirements**
1. Any treatment that allows for certification to Category 1 states is also suitable for certification to Category 2 states. 2. Dip treatment intended to kill larvae (grubs) in containers or B&B. Acceptable for nursery stock in containers and B&B plants that are 32” in diameter or smaller.
- The rooted portion of the container or ball must be completely submerged in pesticide solution for a minimum of 2 minutes or until complete saturation occurs, as indicated by the cessation of bubbling.
- The ambient temperature must be at least 50F at time of dip.
- Upon removal from solution, the plants must be allowed to drain according to label directions.
- During JB flight season (June through Sept.) dip treatments are only good for 2 weeks of certification. If more time passes, an additional treatment would be required.
- Treatments performed outside of the flight season are suitable for certification until the time of the next flight season.
3. Pre-Harvest Soil Surface TreatmentsField grown material of any size may be harvested and certified from fields that are treated prior to harvest in the months of May through July.
- Insecticide must be applied to rows in bands that extend six (6) inches wider than actual root ball diameter to be dug. Do not allow bands in adjacent rows to overlap.
- Vegetation should be mowed to a height of 3 inches or less before application. Do not mow until after sufficient irrigation or rainfall has occurred.
4. Field Grown Nursery Stock Accreditation Program (possibility that treatment would be required)This is a compliance agreement program that allows for certification of field grown material to Category 2 states.
- The program requires the maintenance of a weed-free zone around field plants as well as soil sampling to monitor for beetles.
- Insecticides could be used in this program for treatment of larvae and adults and these are found in the JB-labeled product list.
5. Shipments of sod (lawn or turf-grass) It is possible to ship sod to Category 2 states with compliance agreement. Certification would likely involve the use of both adulticide treatment around periphery of the sod farm and larval treatments of the sod.
Insecticide options are found in the JB-labeled product list.
6. Adult Beetle MitigationDuring flight season between June 1 and September 30th, nurseries are responsible for ensuring that clean stock does not become infected by adults. The JBHP outlines critical control points to monitor. Insecticides that target adults are provided in the JB-labeled product list, to be used for certification if adults are present. There are different insecticides for use on plant material and container (truck/trailer) spaces.