What is an Air Curtain Incinerator?
An Air Curtain Incinerator is a device that burns wood waste, like trees and brush. It has an insulated box to contain the wood waste and a fan powered by a diesel engine that blows a curtain of air over it. Oregon uses ACIs for both fire prevention efforts and wildfire cleanup. They are an alternative to traditional open burning and produce less smoke and particulate matter.
There are two types of air curtain incinerators: the first produces biochar, while the second produces ash. Both are powered by a diesel engine that must meet the cleanest Tier 4 engine standards available on the market.
How the Incinerator Works
- High velocity air is directed into the box
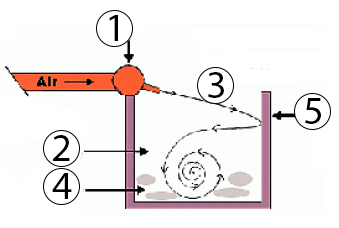
- Continued airflow keeps fire temperature high for more complete combustion
- "Curtain" formed from high velocity airflow
- Material to be burned
- Refractory lined walls (can also be an earthen trench)
What is emitted from an ACI?
Compared to traditional outdoor burning of wood waste, air curtain incinerators emit lower levels of air pollutants, including PM2.5 and nitrogen oxide. They burn more efficiently and produce significantly less smoke than traditional outdoor burning. Only authorized materials can be burned in an ACI and DEQ has created a list of the authorized and prohibited materials.
Toxic air pollutants from ACIs come from the wood itself. Some metals occur naturally in the soil and are taken into the tree through its roots. Then, they can be released into the air when the wood is burned. Emissions from the diesel engine that powers an ACI's fan are also assessed as part of a DEQ air permit. Results from our ACI emissions tests show that toxic air pollutants are relatively low and not a major concern. Learn more on the ACI Emissions Testing web page.
How does the Cleaner Air Oregon program estimate health risk?
Oregon facilities are required to evaluate the health risk from toxic air pollutants. To do this, facilities first estimate the types and amounts of toxic air pollutants emitted. Next, they determine the risk from those toxic air pollutants to adults and children living, working, or going to school nearby. This is done through dispersion modeling that estimates how much of a given pollutant a person nearby may breathe in based on distance, time and amount.
DEQ compares the dispersion modeling estimates of risk with Oregon's established health standards. If the facility's risk is higher, DEQ requires it to reduce emissions.
An ACI is operating near me. What can I expect?
An ACI may emit brief periods of smoke and smell of burning wood when it starts and as operators add new material into it. Noise from the device is limited to the diesel engine and blower fan, as well as the vehicle, such as an excavator, loading the wood.
An ACI should not consistently produce heavy smoke. If it does, that may indicate it's not being properly operated.
ACIs in Oregon
The following companies are currently permitted or are applying to operate in Oregon. If a company is listed as 'portable', they must notify DEQ anytime they move to a new location.
What other rules apply?
There are many safety protocols an ACI operator must follow to protect those in the area. For example, an ACI can't operate if the local fire department or U.S. Forest Service has banned burning; an air stagnation advisory is in place; or the region's Air Quality Index is 100 or greater. An operator must be trained by a certified professional and must follow all safety precautions recommended by the manufacturer.
If you have concerns about the operation of an ACI near you, please contact DEQ.